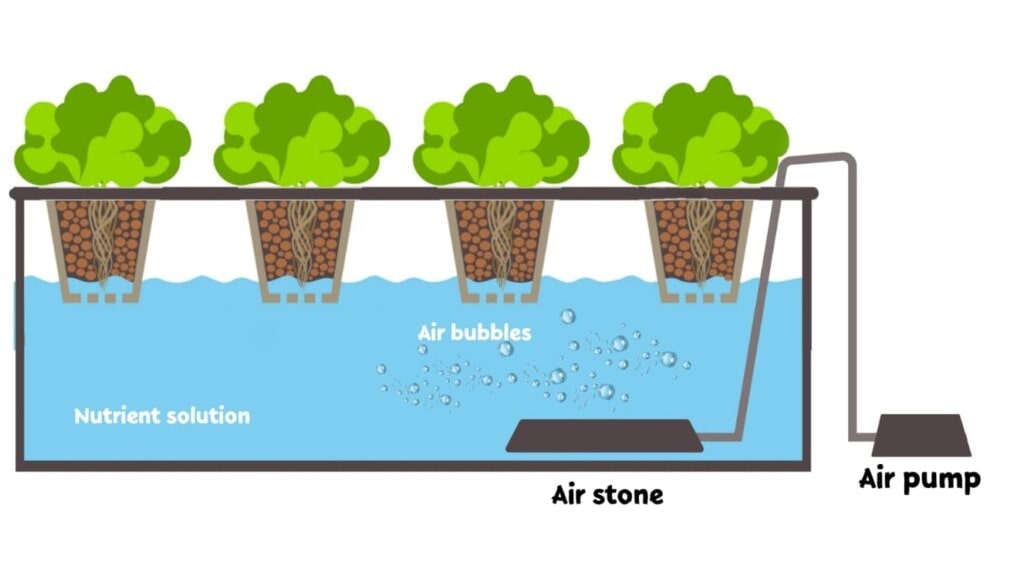
As enthusiasts in the realm of hydroponics, we understand the essential role nutrients play in the thriving of plants. Ensuring the optimal health of your plants means knowing just how long your hydroponic nutrients remain effective. Generally, concentrated hydroponic nutrients remain viable when stored properly for about one to two years, while mixed solutions should be used within 7 to 10 days for optimal results.
Storage methods significantly impact the longevity of these nutrients, so it’s crucial to store them in a cool, dark place, tightly sealed to prevent exposure to air and moisture. Knowing how to manage these nutrients effectively not only saves resources but also ensures your plants get the absolute best of what they need to flourish.
Our guide is here to provide comprehensive insights into the shelf life, storage, and disposal of hydroponic nutrients. Join us as we explore how to extend their usability and discuss whether using expired nutrients is a wise option for your hydroponic setup.
Key Takeaways
- Hydroponic nutrients last one to two years unopened.
- Store in cool, dark places to maximise shelf life.
- Use mixed solutions within 7 to 10 days.
What Is The Shelf Life Of Hydroponic Nutrients?
When it comes to hydroponic nutrients, shelf life can differ based on the type of nutrients and how they are stored.
Liquid nutrient bottles when unopened and stored in optimal conditions, typically have a shelf life of about two years. On the other hand, powdered nutrients often last longer due to their lack of water content, making them more stable over time.
When exposed to light, heat, and air can significantly affect the longevity of these nutrients. That’s why it’s crucial to store them in cool, dark places, ensuring they are tightly sealed to maintain their effectiveness.
Whether you're dealing with a nutrient solution or mixed hydroponic nutrients, these guidelines can help keep your set-up running smoothly. Organic nutrients may have a different shelf life compared to their synthetic counterparts due to natural decomposition processes.
A quick reference can highlight the distinctions:
| Nutrient Type | Shelf Life (Unopened) |
|---|---|
| Liquid Nutrients | Up to 2 years |
| Powdered Nutrients | Longer than liquids |
It's helpful to make sure we're aware of these differences when planning for our hydroponic systems. Proper storage can really make a difference in how long these nutrients last.
What Are The Best Brands?
When we dive into the world of hydroponic nutrients, a few brands consistently stand out for their quality and reliability.
Atami B'Cuzz is a staple in the industry. Known for its comprehensive range of products, it's a favourite among many gardeners. One case study highlighted a gardener's success story using Atami products across multiple growth cycles, praising its consistency.
Next, Advanced Nutrients offers convenient pH-perfect formulas, simplifying the nutrient management process. Their innovative approach makes them a popular choice for both beginners and experienced growers alike.
Fox Farm is also worth mentioning. Although not highlighted in our initial search, this brand is known for its potent organic mixes.
Here is a simple breakdown of what makes these brands stand out:
| Brand | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Atami B'Cuzz | Reliable, comprehensive range, tried-and-tested |
| Advanced Nutrients | pH-perfect, user-friendly, innovative |
| Fox Farm | Organic potency, strong market reputation |
These brands have garnered positive reviews for their longevity and effectiveness. Users frequently testify to their satisfaction, noting how their gardens thrive with these nutrient solutions.
Can You Use Expired Plant Nutrients?
In our hydroponic adventures, we've all wondered if we can stretch our supplies a bit further. One of the big questions is whether we can still use expired plant nutrients.
Assessing Nutrient Viability:
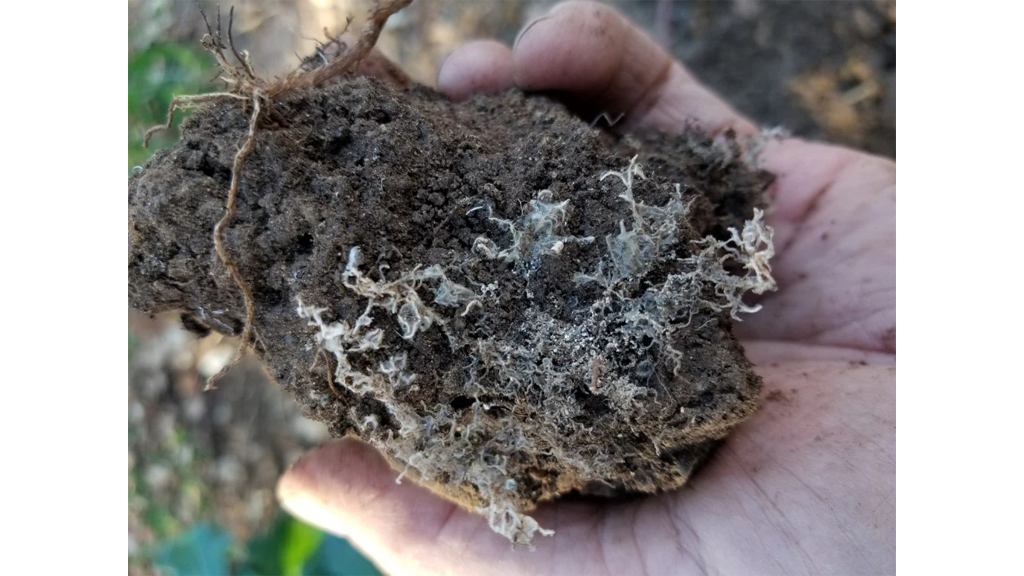
Before you decide, it's crucial to evaluate the state of the nutrients. Look for visual indicators such as separation, discolouration, or unusual odours. These can suggest that the nutrients are past their prime. Another useful step is testing the pH and electrical conductivity (EC) of the nutrient solution. This can help determine whether the solution still offers sufficient nutrients for plant growth.
Potential Risks of Using Expired Nutrients:
Let's consider what could happen if we use expired nutrients. One major concern is reduced nutrient availability, which might result in suboptimal plant growth. There’s also a risk of introducing pathogens or contaminants, potentially harming our plants.
Expert Recommendations:
Not surprisingly, many experts suggest that when in doubt, it's best to discard expired nutrients. Doing so ensures our plants receive the full spectrum of nutrients they need to flourish. In the long run, this approach typically saves us time and reduces heartache from stunted or unhealthy plant growth.
Taking these precautions into account, we can make more informed decisions about our nutrient choices and help our plants grow as robustly as possible.
How To Dispose Of Hydroponic Nutrients
Disposal of hydroponic nutrients requires careful consideration to ensure safety and environmental responsibility. It's vital to adopt proper disposal methods to protect our environment.
Safe Disposal Methods:
-
Dilution: One effective way is to dilute small amounts of nutrients with water. We can then use this solution to fertilise outdoor plants, thereby minimising waste.
-
Consultation: For larger quantities, it's advisable to contact local waste management facilities. They provide guidelines tailored to local regulations and ensure that we're adhering to safe practices.
Environmental Considerations:
We must avoid dumping nutrients into waterways. This can lead to ecological imbalances and harm aquatic life. Adhering to local regulations on chemical disposal is crucial. These rules are in place to protect our natural surroundings and promote sustainable practices.
Summary of Tips for Disposal:
- Dilute with water for small-scale use.
- Seek guidance for disposing of larger amounts.
- Avoid waterways to prevent ecological disruptions.
- Follow local chemical disposal regulations.
Disposing of hydroponic nutrients correctly helps maintain a healthy ecosystem and ensures compliance with environmental safety laws. We must all play our part in preserving our planet's delicate balance.
Conclusion
Hydroponic nutrients are a vital part of any successful hydroponic garden. Their shelf life can vary but generally ranges from several months to two years, depending on factors like the type of nutrient solution and storage conditions.
Proper storage methods are crucial. Keeping nutrients in a cool, dark environment can extend their lifespan and maintain their effectiveness.
We should always consider the importance of monitoring nutrient quality regularly. This ensures that our plants receive the right balance of nutrients they need to thrive.
Disposal of expired or degraded nutrients should be handled cautiously to prevent any environmental harm. It's important to follow local regulations for safe disposal practices.
We invite you to share your insights and experiences regarding nutrient management. Your tips could be invaluable to fellow hydroponic gardeners.
By staying vigilant and proactive, we can all enjoy a thriving hydroponic garden. Let's work together to achieve success in our gardening journeys!






 Store Locator
Store Locator